Networks and Security
1. Introduction
Computer Network is a group of two or more computers or other devices, connected to each other for the purpose of exchanging data or sharing common peripheral devices (e.g., a printer in some office), files (e.g., patient file in a hospital) and software (e.g., customer service program in store). A network can only extend to one room, one building, to buildings within a few kilometres, within a city, between several cities, within a country or several countries. On the basis of the geographical area covered, the networks are classified into two categories:
• Local Area Network-LAN: is a network within one or more rooms, a building or even between nearby buildings. It connects computers to a limited geographical area coverage zone.
• Wide Area network - WAN networks: usually, they connect several local networks together and cover a large (wide) geographical area. Public telecommunications lines or, sometimes, satellite telecommunications are almost always used for this interconnection. These networks may extend within a city, between cities of a country or in cities of different countries.
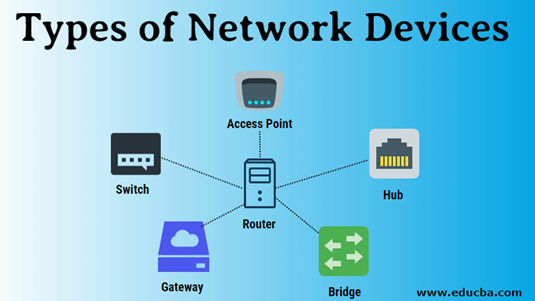
2. Networking devices
To create a network of computers and other devices, special networking equipment is needed, as shown below:
• Network Interface Card, NIC : Device that is usually installed inside the computer and connects the computer to a computer network. The connection can be made by wire or wirelessly
• Switch: Device with multiple ports (16-ports, 24-ports) that connects computers and devices, one/one to each port, using cables and allowing them to exchange information to form a network. The corresponding device for connecting to a wireless network is called a wireless access point
• Router: Device that connects a local network to the Internet or several networks together. It is responsible for routing (sending in the right direction) data along multiple networks
• Modem: Device that connects the computer or other device to an analog telephone line. Its purpose is to convert the digital signal (information) of the computer to analog and vice versa (Modulation/Demodulation), so that it can be transferred via an analog telephone line.
3. Network and Internet risks, security and protection measures
It is often stated that the use of networks poses risks to the user and computers/devices. Here, we will consider, mainly, the risks associated with problems of the device, but for which protection measures can be taken with settings or software installation.
4. Protection of wireless networks
With the widespread use of wireless networks, the need to protect the wireless network and the data transferred from it arises. Many times, non-qualified personnel purchase and install wireless equipment (router or wireless access point). Once the equipment is installed, it is set by its manufacturer with standard values. These are known to anyone and can easily connect to our wireless network, either to gain access or to intercept our data. For this reason, we must adjust the equipment at least by specifying the following settings with values of our own choice:
• The password (password) of the administrator (administrator) of the equipment.
• The name of the wireless network (SSID).
• Wireless network security settings. Avoid the WEP encryption / certification which does not provide much security and prefer WPA2. Also, we make sure the key phrase (passphrase/key) is difficult to be discovered using at least 8 characters, uppercase and small letters, numbers and symbols.
• Disable SSID Broadcast. This has as result that our network is not located in the available wireless networks and only those who know its name can connect
5. Updating the operating system and applications
Often, security gaps and other problems are found in both the operating system and applications, in particular web browsers (Internet Explorer, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Safari, etc.) Systematic and frequent updating is recommended for both the operating system and these programs, so the exploitation of security gaps by intruders in the system and malicious programs is prevented.
6. Firewall Installation
Firewall is software (program) or material (device), which is accordingly configured, so to allow or reject data packets that they pass from one computer network to another. Firewall protection may prove useless if not configured right.
To enable /disable the Windows Firewall, we can to follow the following steps:
• We activate the Control Panel.
• Click on Network and Internet.
• Click on Network and Sharing Center.
• Click on Windows Firewall.
• Click on Turn Windows Firewall on or off.
• In the framework below we make the appropriate choices.
• click OK

6. How to create a strong and secure password:
According to traditional advice a strong password:
• It has 12 characters, Min: You must choose a password that is long enough. There is no minimum password length that everyone agrees on, but generally you should choose passwords that are at least 12 to 14 characters long. A longer password would be even better.
• Includes numbers, symbols, uppercase and lowercase letters: Use a mix of different character types to make the password harder to crack.
• It's anything but a word reference word or a mix of word reference words: Stay away from clear word reference words and word reference word blends. Any word without anyone else is awful. Any mix of a couple of words, particularly in the event that it is self-evident, is likewise terrible.
• Doesn't Rely on Obvious Substitutions: Don't utilize normal replacements, either — for instance, "H0use" isn't solid since you've supplanted an o with a 0. That is simply self-evident.
Attempt to blend it up—for instance, "BigHouse$123" fits a significant number of the prerequisites here. It's 12 characters and incorporates capitalized letters, lower-case letters, an image, and a few numbers. Be that as it may, it's genuinely self-evident—it's a word reference express where each word is promoted appropriately. There's just a solitary image, every one of the numbers are toward the end, and they're in a simple request to figure.EXERCISES:
1. Answer the following questions:
a. What is networking?
b. Define Network devices.
c. Differentiate between LAN and WAN.
d. Define a peer-to-peer network.
e. What is communication medium?
2. Go ahead and create your own password. How would you be able to deal with limiting the dangers to your remote organization? Make a list.